How to Set Up and Manage Buyers
Updated 20 months ago
Creating a Buyer
To create a buyer, you need to click the "Create" button and enter the buyer's name.
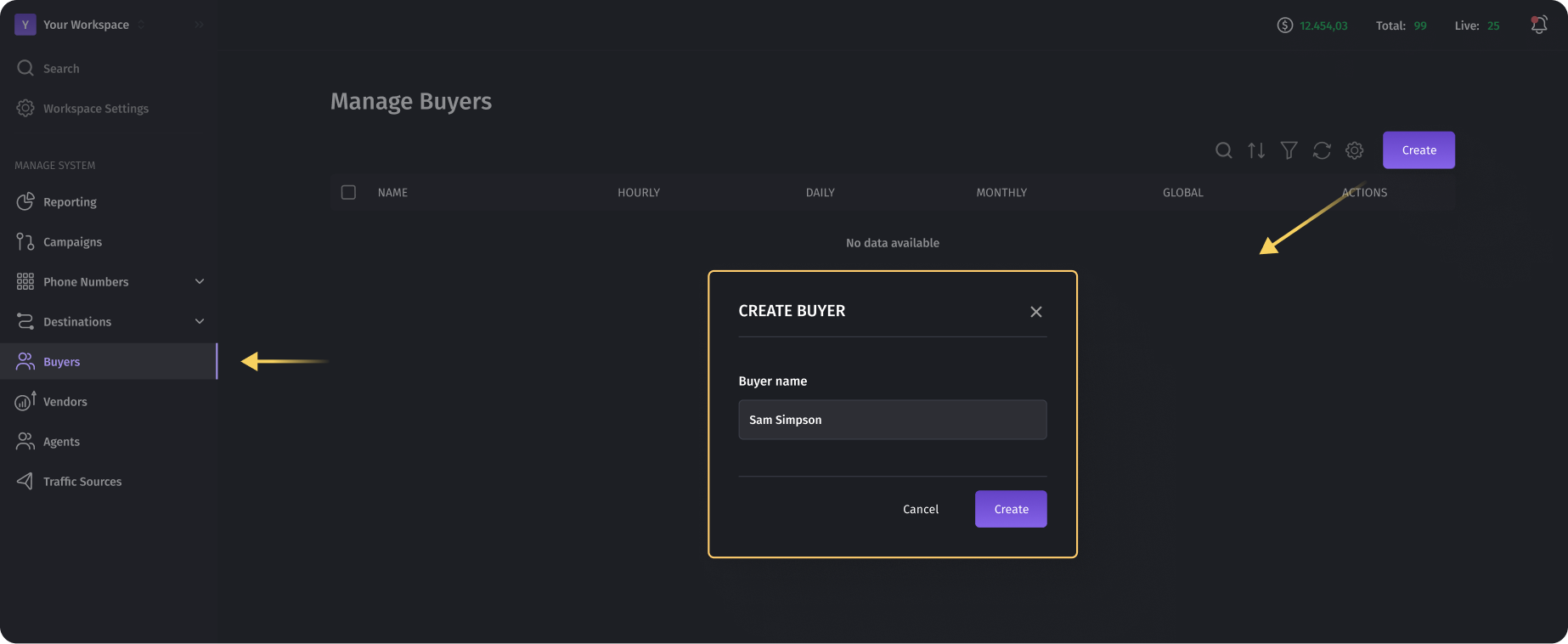
Set up Buyers
Afterward, the newly created buyer will be open for editing, allowing you to configure it in more detail.
Further settings include:
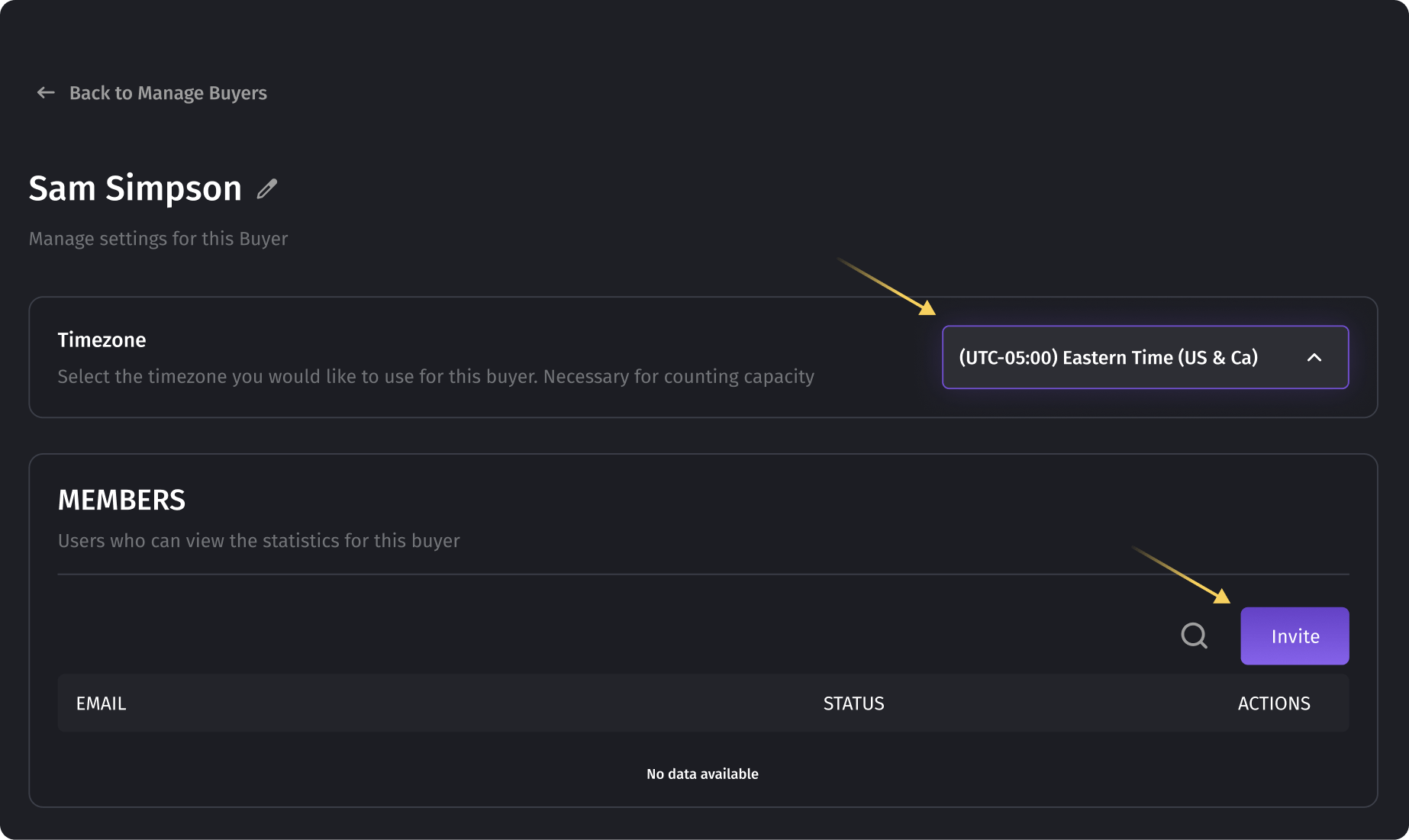
- Choosing a time zone for the buyer. This parameter only affects the calculation of limits for the buyer. If you don't intend to set limits for the buyer, you can skip this setting. However, we recommend configuring it correctly to avoid errors in the future.
- To invite users under this buyer, you need to click on the "Invite" button and enter the user's email. You can enter multiple emails. Afterward, they will receive an email with a link to create an account in the system.
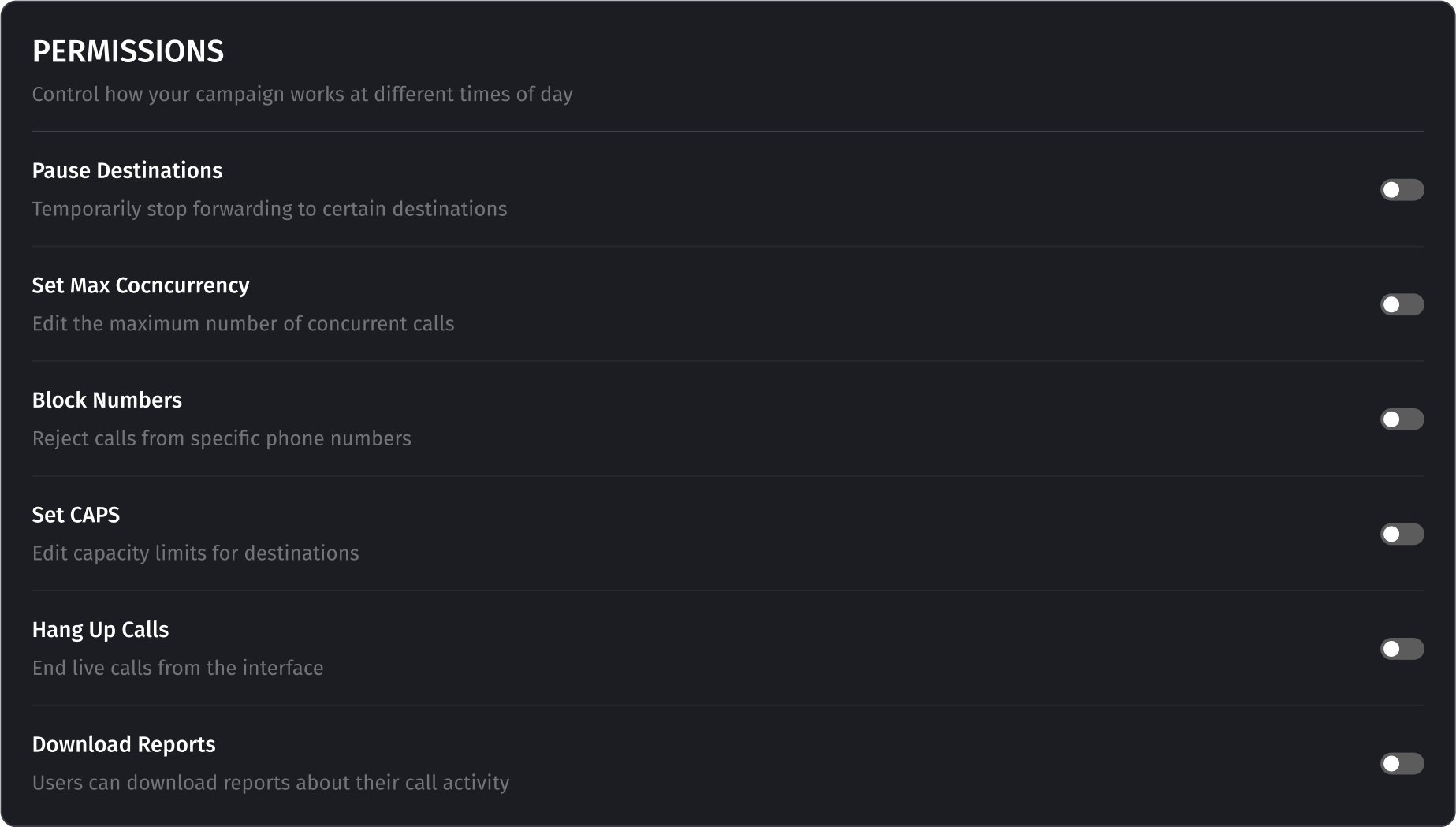
Permissions for Buyers
Managers of the account can set certain permissions for users invited under a buyer:
- Pause Destinations The manager can allow the Buyer to change the status of destinations related to it, pause, stop, or start it which gives a possibility to regulate the work of its agents. After all, if an agent is unavailable and a destination is active, the system will continue to send calls to it, and this may result in non-connected calls.
- Set Max Concurrency Under a single destination phone number, there can be an entire call center with a specific number of agents. Typically, any customer support service has a unified number and a certain number of agents. When a call comes to this number, the internal system redirects the call to one of the available agents. The buyer can specify how many agents are currently available to take calls. If the buyer specifies an incorrect number (for example, more agents than are available), the system will direct calls to this destination, and they will either be put on hold in the call center or dropped, resulting in a loss.
- Block Numbers Sometimes there is a need to block calls from a specific number, such as in the case of spam or pranks. Such calls disrupt normal operations, quickly deplete daily call limits, and need to be addressed.
- Set CAPS Buyers can limit the number of calls to each destination. For example, they may want one destination to answer only 25 calls per day. The system constantly checks and monitors all limits, and if they are reached, it stops directing calls to that destination.
- Hang Up Calls Sometimes there is a need to terminate a phone call, as some agents may linger too long with a client. To avoid spending money on talk time, the buyer can forcibly end a particular call.
- Download Reports (CSV) When this option is enabled, the buyer has a button to download the call log and aggregated data on the Reporting page.
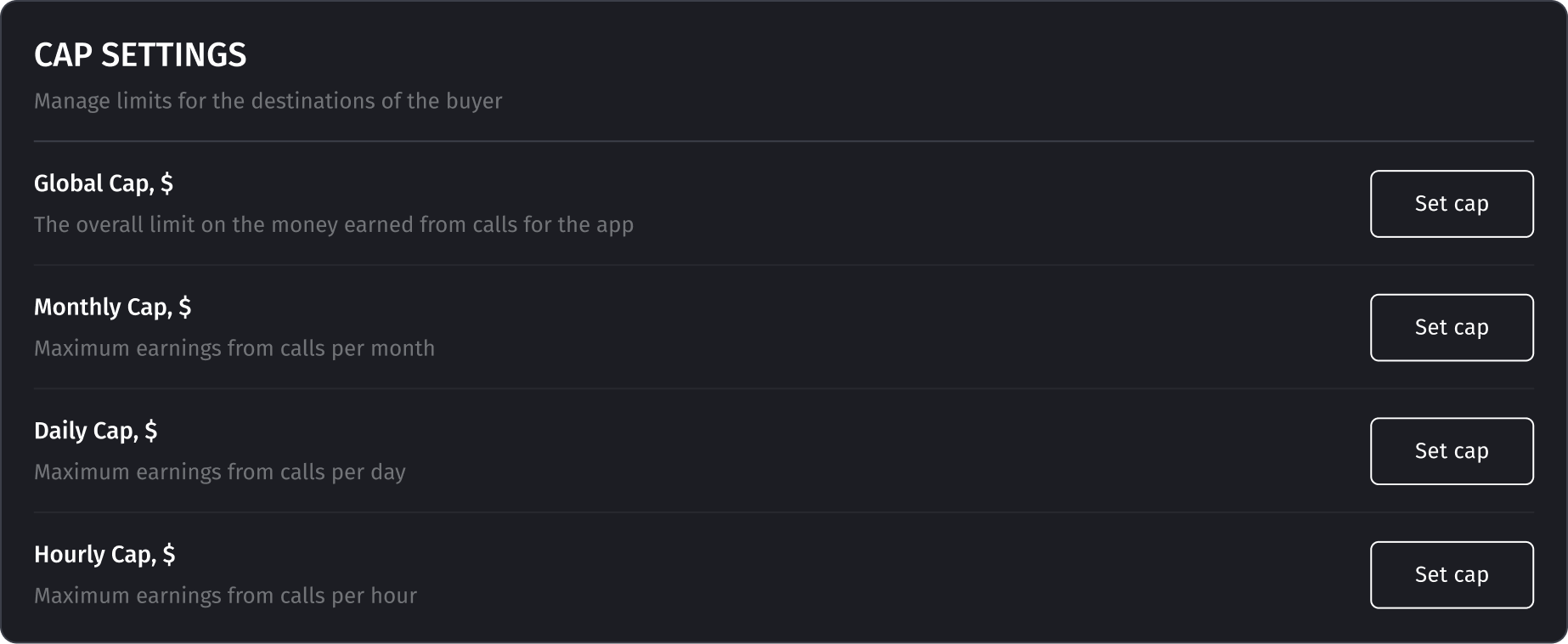
CAP settings
Configuring limits for a buyer is crucial, especially when the buyer has a limited budget for lead purchases.
- Global Cap: This limitation takes the highest priority. Once it is reached, the destination will cease to accept calls indefinitely until the limit is reset or disabled.
- Monthly Cap: Monthly limit, reset every month.
- Daily Cap: Daily limit, reset every day.
- Hourly Cap: The hourly limit is reset every hour.
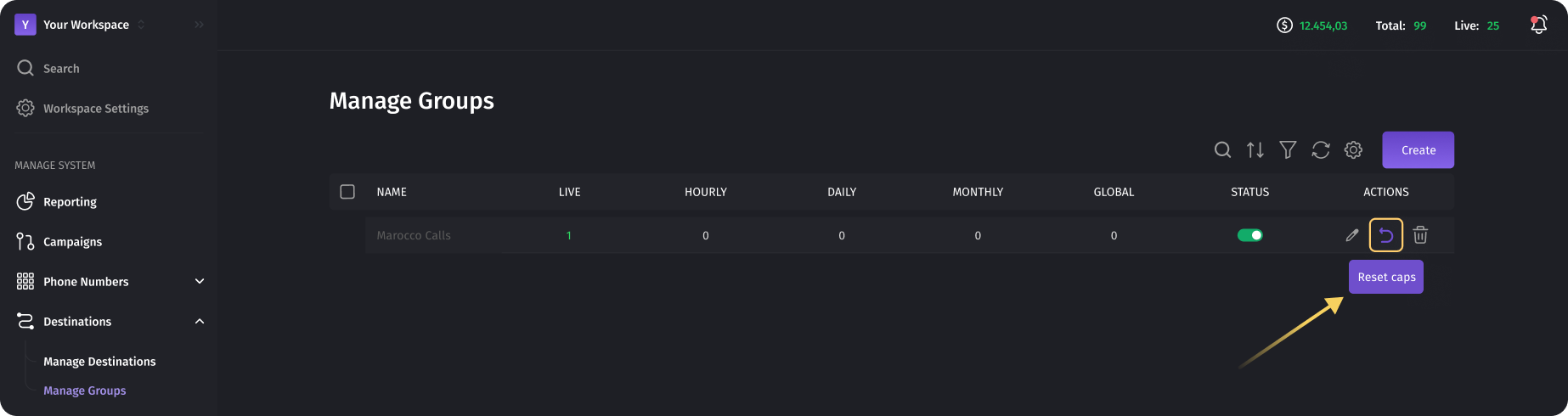
To reset all counters, you need to press the "Reset Caps" button. This action will result in a complete reset of all counters(calls), including hourly, daily, monthly, and global counters, setting all values to zero.
Calculating the Limits
In the Dialics system, limits are calculated as follows:
If you set a daily purchase limit of $500, Dialics will consider the total revenue from each destination for that buyer.
Let's assume the buyer has three destinations, each configured with a revenue of $25.
- The first destination received 4 converted calls: 4 * $25 = $100.
- The second received 12 converted calls: 12 * $25 = $300.
- The third received 4 converted calls: 4 * $25 = $100.
The total sum is $500. After reaching this point, the Dialics system will stop sending calls related to this buyer to prevent exceeding the set daily limit of $500. Be cautious when setting limits, as it could lead to call loss if the limit is quickly reached.
Was this article helpful?